The Art of Prompt Engineering- Part 2
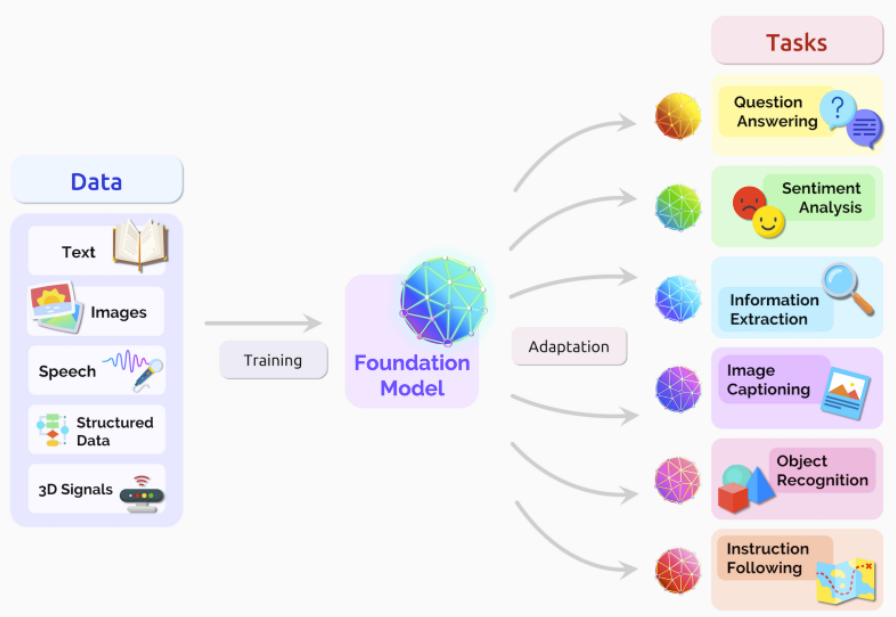
Welcome to the second part of our three-part series on the exciting world of Prompt Engineering. In Part 1, we explored the fundamentals of Prompt Engineering, the building blocks and signs behind prompt engineering, and the ethical considerations involved. In this instalment, we will dive deeper into a comprehensive array of techniques that can elevate your prompt engineering skills to new heights, real-world examples, and case studies that highlight the transformative power of prompt engineering. Get ready to unlock the full potential of this fascinating field!
Advanced Techniques in Prompt Engineering
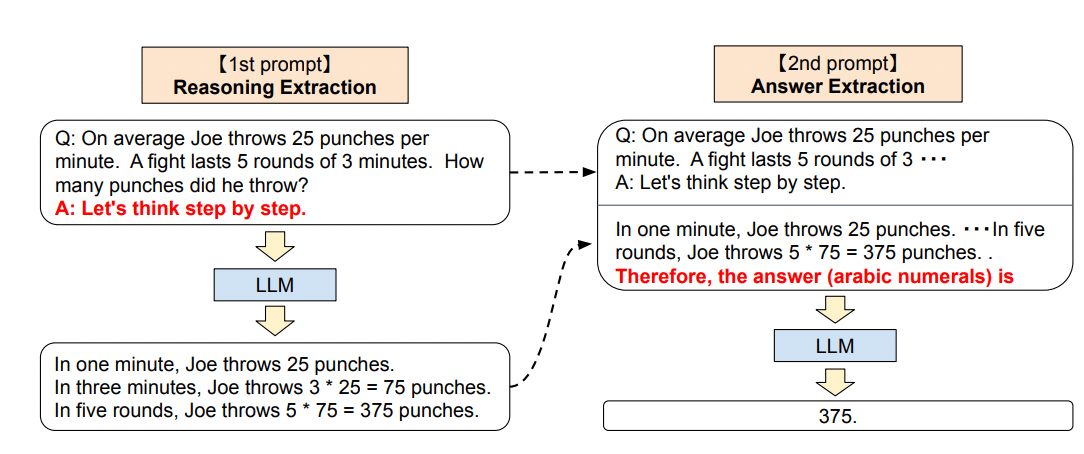
Building upon the foundation established in Part 1, let's explore advanced techniques and strategies for enhancing prompt engineering:
Zero-Shot Prompting
Zero-shot prompting allows you to elicit responses from AI models for tasks they have not been explicitly trained on. By providing a prompt that specifies the desired output format and task description, you can leverage the general knowledge and capabilities of the AI model to generate responses. This technique is beneficial when exploring novel tasks or obtaining high-level insights from AI models without extensive fine-tuning.
Few-Shot Prompting
Few-shot prompting enables you to train AI models with limited examples or demonstrations. By providing a few instances or prototypes of the desired behaviour, along with corresponding prompts, you can guide the model to generalise and produce similar outputs for similar inputs. This technique is valuable when you have limited labelled data and need the model to learn from a small amount of information.
Chain of Thought Prompting
Chain of thought prompting involves creating a sequence of prompts that guide the AI model to reason or think step by step. You can navigate the model through a logical reasoning process by breaking down complex tasks into smaller subtasks or questions. This technique is useful when you prompt the model to generate outputs requiring multi-step thinking or sequential decision-making.
Self-Consistency Prompting
Self-consistency prompting aims to encourage AI models to generate coherent and consistent responses. By framing prompts that explicitly ask the model to ensure coherence within its generated output, you can improve the quality and reliability of the responses. This technique is essential when generating outputs requiring logical consistency, such as story generation or fact-checking tasks.
Generate and Rank Prompting
Generate and rank prompting involves prompting the AI model to generate multiple potential responses and then rank them based on criteria or preferences. By providing prompts that ask the model to create and evaluate alternative options, you can obtain a more diverse range of responses and select the most suitable one. This technique is valuable when exploring possibilities and selecting the best outcome from multiple choices.
Knowledge Prompting
Knowledge prompting allows you to prompt the AI model to generate responses demonstrating a specific knowledge or expertise level. By incorporating domain-specific facts, concepts, or references in the prompts, you can guide the model to produce outputs that align with the desired level of expertise. This technique is beneficial when you want the model to generate knowledgeable and accurate responses in specialised domains.
Automatic Reasoning and Tool Use
Automatic reasoning and tool use involve designing prompts that explicitly instruct the AI model to perform logical reasoning or utilise specific tools or strategies to generate responses. By incorporating logical rules, deductive or inductive reasoning cues, or references to external resources, you can prompt the model to generate outputs that demonstrate sophisticated reasoning capabilities. This technique is useful when you want the model to exhibit advanced logical thinking or utilise specific methods to solve complex problems.
Real-World Examples of Prompt Engineering in Action

Let's explore how prompt engineering is being employed in various domains to solve complex problems and drive innovation:
- Healthcare: Prompt engineering is revolutionising healthcare by enabling AI models to provide accurate medical information, diagnose, and offer personalised treatment recommendations. Medical professionals can leverage prompt engineering to access up-to-date research, guidelines, and insights, enhancing patient care and outcomes.
- Education: Prompt engineering is transforming the way we learn and teach. AI models can generate interactive lessons, provide personalised feedback, and assist in automating administrative tasks. Educators can leverage prompt engineering to create engaging and tailored student learning experiences.
- Data Analysis: Prompt engineering is proving invaluable in data analysis. Researchers and analysts can gain actionable insights and make data-driven decisions more efficiently by crafting prompts that guide AI models to analyse and interpret complex datasets.
Case Studies: Successful Applications of Prompt Engineering
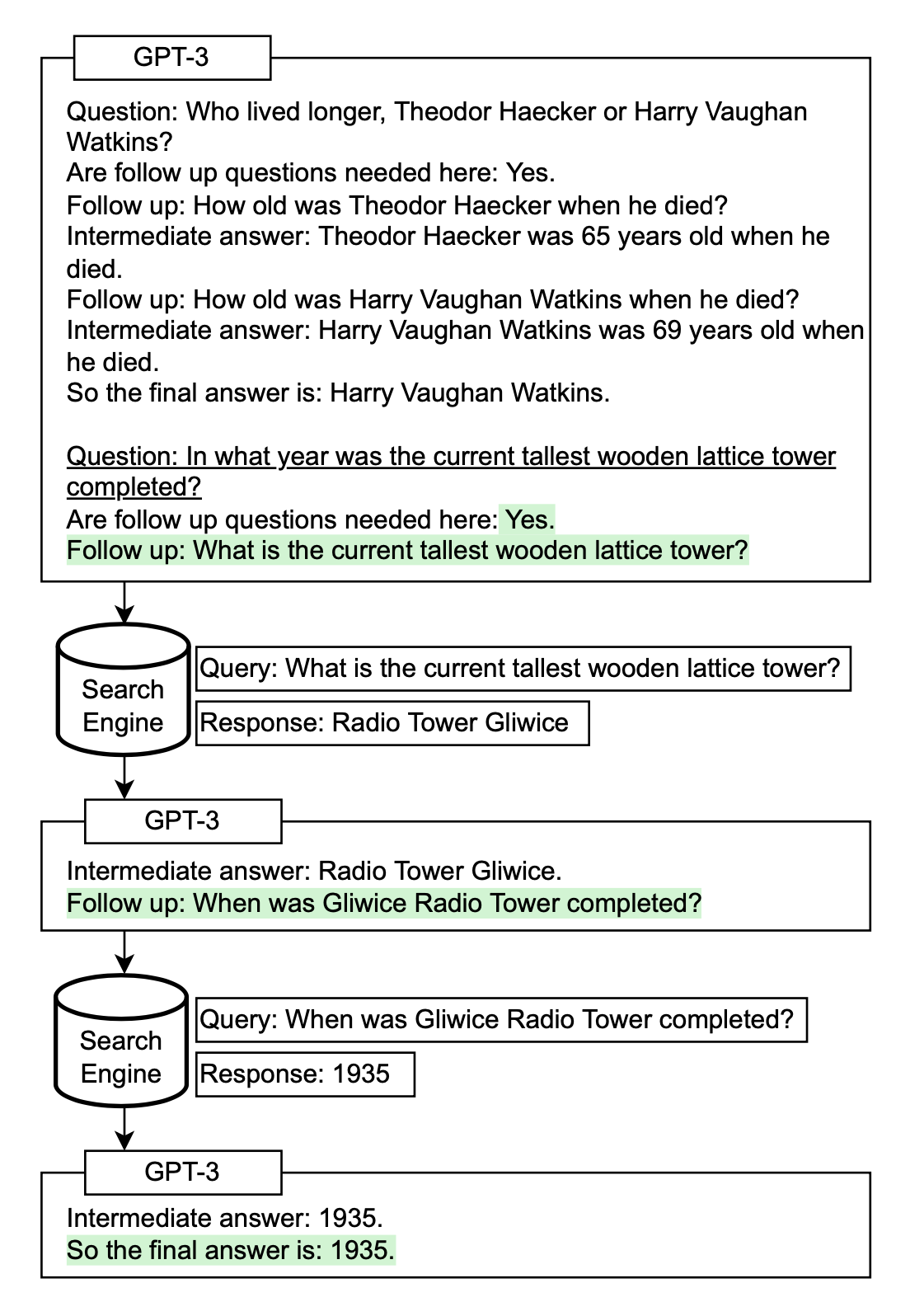

Let's explore a few case studies that demonstrate the power of prompt engineering in real-world scenarios:
- Virtual Assistants: Prompt engineering has enabled virtual assistants to understand and respond to user queries with greater accuracy and relevance. Through practical prompt engineering, virtual assistants have become indispensable in providing personalised recommendations, assisting with tasks, and delivering information tailored to individual preferences.
- Content Generation: Prompt engineering has empowered creators by enabling AI models to generate high-quality content in various domains. By providing prompts that specify tone, style, and subject matter, AI models can assist in creating engaging blog posts, social media captions, and marketing materials.
- Language Translation: Prompt engineering has revolutionised the field of language translation by enabling AI models to produce more accurate and natural-sounding translations. AI models can provide reliable and contextually appropriate translations by designing prompts that incorporate the nuances of different languages and cultural contexts.
- Customer Support: Prompt engineering has transformed customer support services by enabling AI models to effectively understand and address customer inquiries. By designing prompts that capture the key information needed to resolve customer issues, AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide prompt and accurate support, improving customer satisfaction and reducing response times.
- Financial Analysis: Prompt engineering plays a significant role in financial analysis. AI models can be prompted to analyse vast amounts of financial data, identify patterns, and provide insights for investment decisions. By crafting prompts that specify the financial metrics necessary or specific analytical tasks, prompt engineers can help financial analysts extract valuable information from complex datasets more efficiently.
- Fraud Detection: Prompt engineering techniques are instrumental in fraud detection and prevention. AI models can be prompted with specific indicators or patterns associated with fraudulent activities, enabling them to identify suspicious transactions or behaviours in real-time. Prompt-driven fraud detection systems help financial institutions, and online platforms protect themselves and their users from potential threats.
- Personalised Recommendations: Prompt engineering enables AI models to deliver highly personalised recommendations across various industries. By designing prompts that capture user preferences, past behaviours, and demographic information, AI-powered recommendation systems can provide tailored suggestions for products, services, movies, music, and more. These personalised recommendations enhance user experiences and increase customer engagement.
In a Nutshell
Part 2 of our series has delved into advanced techniques, real-world examples, and case studies showcasing the transformative power of prompt engineering. We have explored how contextual prompts, multi-modal inputs, and reinforcement learning techniques enhance AI models' capabilities. Furthermore, we have seen how prompt engineering drives innovation across diverse fields such as healthcare, education, and data analysis. In the final part of our series, we will discuss future trends in prompt engineering.
Looking ahead, the future of prompt engineering holds tremendous potential. Advancements in natural language processing, machine learning, and AI research will continue to shape the field, unlocking even more sophisticated prompt engineering techniques and tools. With ongoing developments, we can expect AI models to become increasingly adept at understanding and responding to prompts, leading to further improvements in their capabilities and performance.
How much is a great User Experience worth to you?
Browsee helps you understand your user's behaviour on your site. It's the next best thing to talking to them.


