Agile Testing
‘Agile’ has become one of the buzzwords in software development industry and many organizations have accepted agile as the preferred choice for project management replacing the traditional waterfall model. Look for any testing job opportunities Job description in job portals–
‘Experience in agile testing’ has become one of the most sought-after skill for testers.
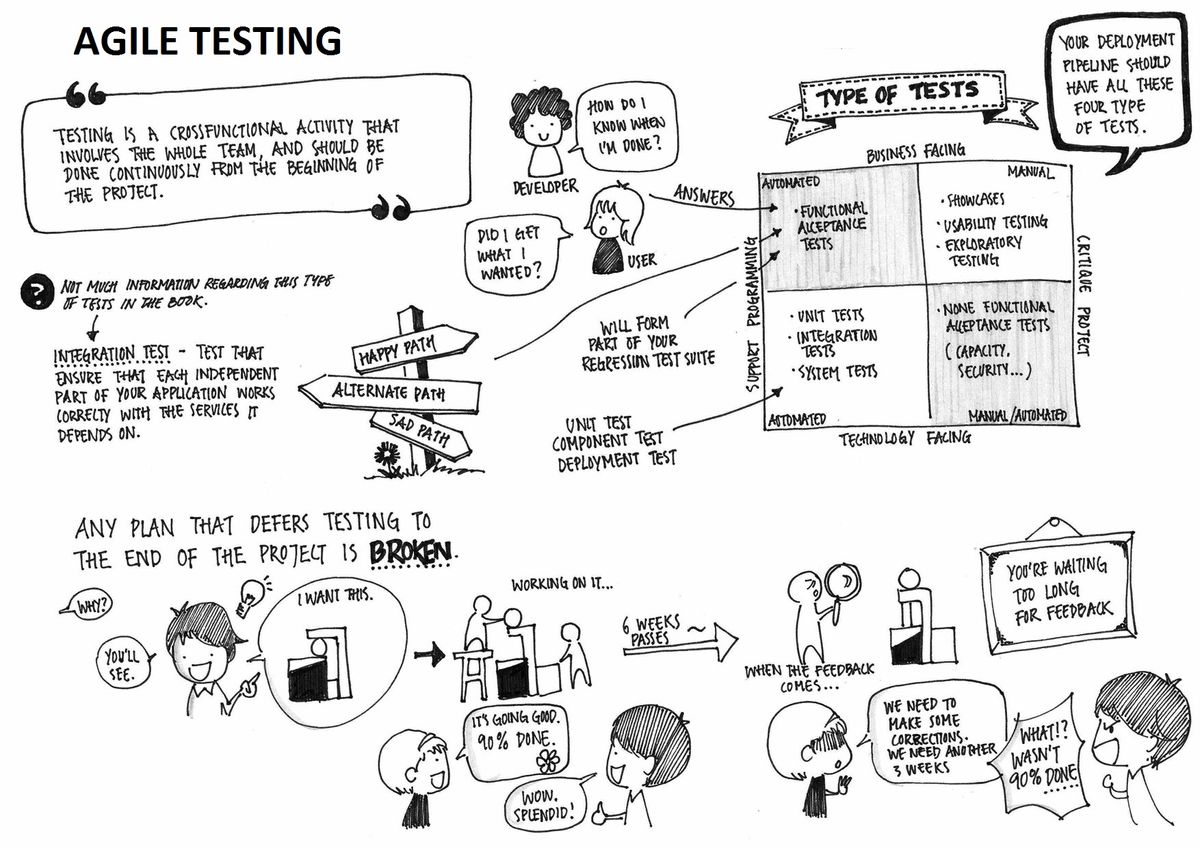
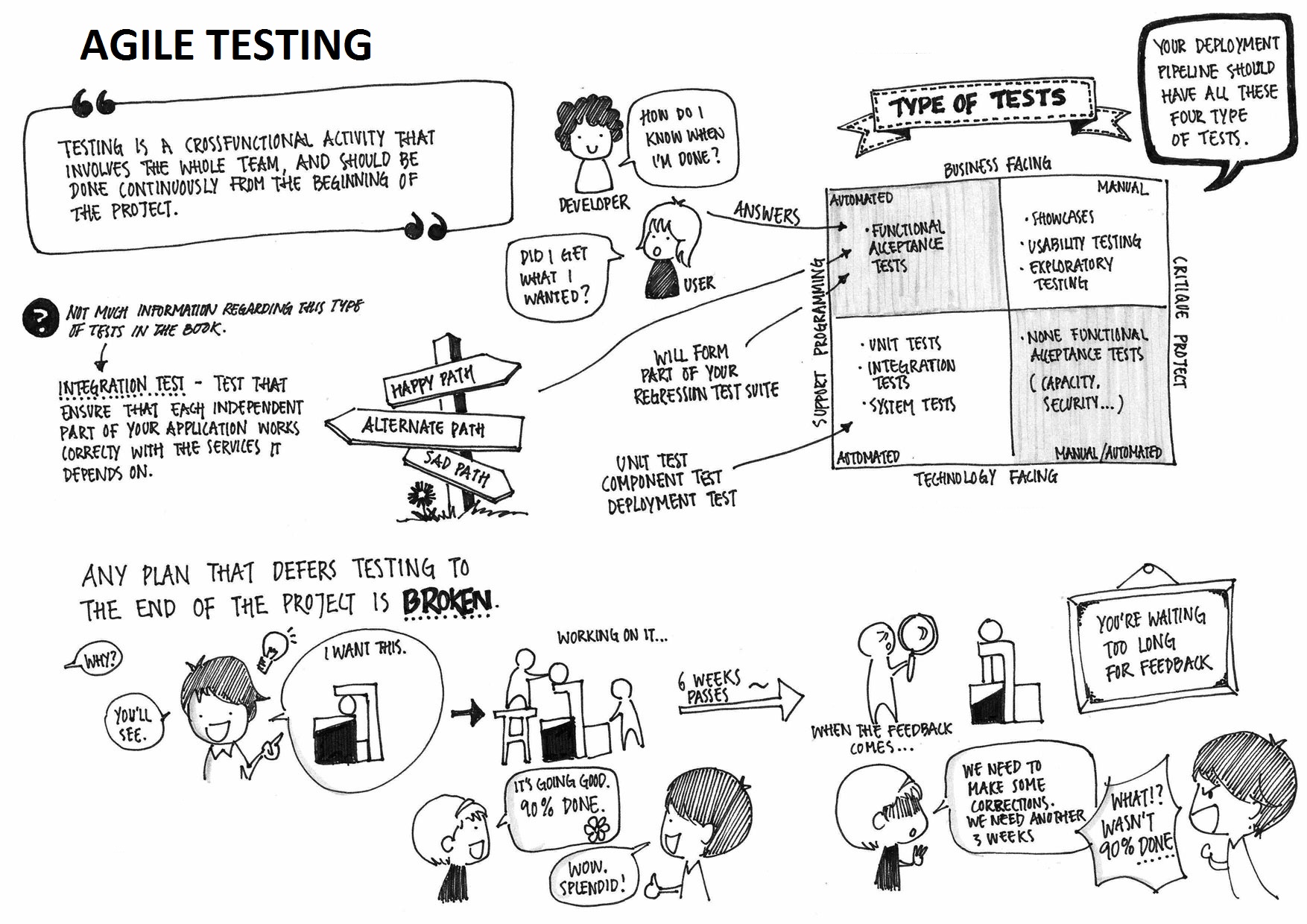
The agile methodology focuses on delivering quality products in shorter time frames. So testing of the software also has to be done in the short time span. As you know, in a traditional waterfall model, testing is conducted only towards the end of the software development lifecycle. This causes significant delays between when the software is written and development receives feedback and the defect identified late in the cycle can affect the product quality. But the agile methodology cannot go by this. Testing has to be done as early as possible in the cycle and demands development and testing activities to be carried out alongside. So testing in an agile environment requires a completely different approach as compared to tradition testing methods. In this article, we will see more about agile testing, how exactly testing fits into agile methodologies and the testing methodologies for an agile environment.
What is Agile Testing?
Agile testing is simply the testing process that follows the principles of agile software development and aligns with the iterative development methodology in which requirements develop gradually from the customers. The main difference between agile testing and the waterfall testing model is that agile testing begins from the start of a project and there will be an ongoing interaction between testing and development. The ultimate aim of agile testing is to deliver a high-quality product within the restricted time frame.
The agile methodology aims in pushing quality products out quicker and consistently into the market. This fast pace of agile poses several challenges to QA in terms of the testing in the shorter time frames available and at the same time deliver quality. The agile testing approach is an effort to overcome these challenges by incorporating the agile principles. Agile principles, as you know are all about being collaborative, flexible and adaptive. To test in an agile environment, testers really need to embrace an agile style of working to cope up with the frequent releases and changing requirements in iterations.
Agile testing definitely comes with an entirely different approach which offers more agility compared to waterfall model of testing. Let’s now have a look at the major differences and how the agility is achieved in agile testing.
- In agile testing, testing is not a ‘Phase’ as in waterfall model. It goes alongside development and testing is continuous.
- The testers in an agile environment need to be highly communicative with the development and business teams to help deliver a quality product in the short time frame.
- Agile testing gives importance to working software rather than complex documentation. Re So testing is the primary task and there is less test documentation.
- Agile testing provides feedback on an ongoing basis to ensure the quality of the product continuously. Daily stand up meetings, design discussions, and reviews with user story verification are all opportunities for giving and receiving feedback.
- An agile model follows a test-driven approach where testing is performed at the time of implementation rather than testing after implementation as in traditional models.
- In agile testing, testers have to be highly cross-functional and adaptable to changes. For achieving the fast pace delivery, increased use of automation, testing techniques such as exploratory testing may have to be incorporated.
Agile Testing approaches
There are various approaches or methodologies for agile testing which enables to achieve the ‘agility’ required for frequent releases in an agile environment. Agile software projects aimed at preventing defects or catching them earlier in the life cycle rather than catching them later in the life cycle. Thus, an agile project requires you to have a shift left test approach (or test-first approach) where testing is performed earlier in the life cycle. This has led to different development methodologies like Test-driven development, Behavior-driven development, Acceptance test driven development, etc. These techniques are used to design requirements and test cases which can be automated using different tools. These methodologies require an entirely different testing approach as well – the way testers write and run tests. Let’s now take a look at these methodologies.
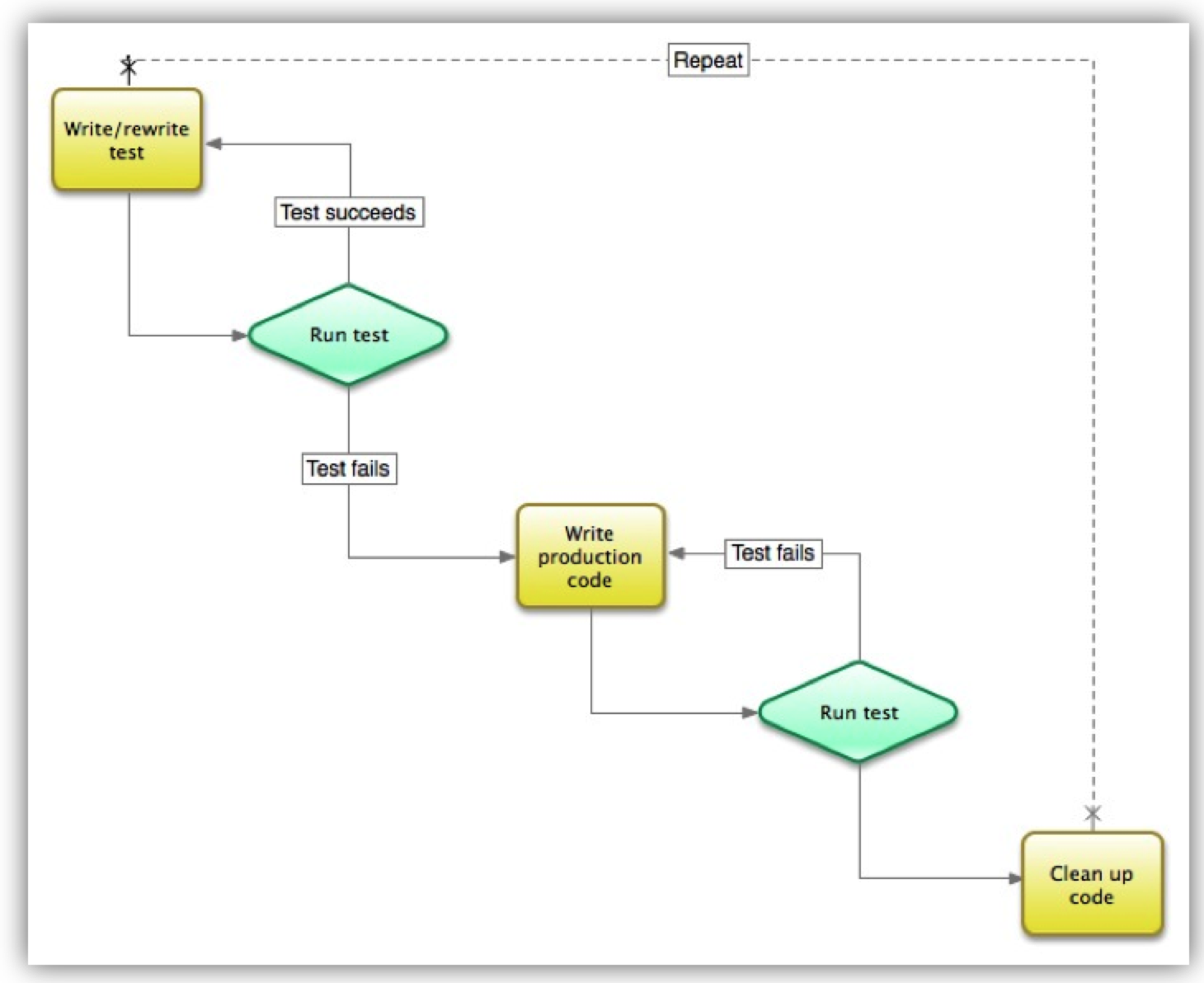
Test Driven Development (TDD)
The traditional approach for testing as you all know was test last approach (write code and then test). But TDD is development method using a test-first approach where you write test and then code. Here the developer designs and writes unit tests for a given code module before writing code and then creates the code with the goal of passing the test.
This approach helps the developer understand the desired result before writing code. In case a defect is found, the developer creates a test to reveal that defect and modify the code so that the test case passes. TDD process can be summarized in the following steps:
- Add a test: In the first step, the developer takes a requirement and turn it to a test.
- Run the test to make sure it fails: Run the test. The test definitely fails as the developer has not developed code for the new test. If the test passes, that means the required behavior already exists.
- Write the code – Now, the developer needs to write the code to make the test pass.
- Run test – Run tests to check if the developed code works.
Acceptance Test Driven Development (ATDD)
ATDD is a development approach which defines acceptance criteria and acceptance tests during the creation of user stories, early in the development cycle. This approach encourages collaboration among the customer, developer, and tester. The acceptance test is written from the customer’s perspective and functions as a requirement to how the software should function and drives the development process.
Behavior Driven Development(BDD)
BDD is an extension to the Test Driven Development (TDD). In BDD, you frame your tests so that they test the application behavior and not specific scenarios. BDD approach tries to answer the questions- ‘Where to start?’, ‘What to test?’ and ‘What not to test?’. BDD starts with a functional specification in the Given-When-Then syntax normally referred to as the Gherkin syntax. It describes the user story in a framework like: Given some initial context, When an event occurs, Then ensure the outcome. The Gherkin text is written such that anyone can understand it. This enables technical as well as nontechnical people involved in the release of the software to understand the test cases.
To sum up, you can see that the requirement is based on behaviors that the product should exhibit and this specification guides the developers, testers and product owners to move across features and build the functionality incrementally guided by the expected behavior.
BDD, TDD, and ATDD are development methodologies which give testing a different dimension from the traditional model. They are mostly used in agile projects as they give a fast feedback for requirements and code under development. These methodologies help you have maximum test coverage.
Apart from these methodologies, Exploratory testing and Session-based testing are two important testing approaches often implemented in agile projects. While, TDD, BDD, and ATDD were development methodologies with a different test approach, exploratory testing and session based testing are functional testing techniques used in the agile environment. Let’s have a look at these as well.
Exploratory Testing
Exploratory testing involves testing an application in a chaotic but still organized way. In exploratory testing, testers usually don’t follow pre-written steps for executing test cases, rather test in clever ways and try to find defects. Exploratory testing is more based on the tester’s knowledge of the software application and there is less documentation. Exploratory testing is best suited when there are time constraints as it can help reduce the time spent testing, find more defects and improve the code coverage.
One other main advantage of exploratory testing is that the unscripted testing often mimics real life user experience and enables testers to get creative with testing. This can sometimes help identify defects that might not have been caught using scripted testing.
But note that exploratory testing can be part of agile testing, but should not be the only form of testing in any project.
Session Based testing
Session-based testing approach is an approach which gives more structure to testing compared to exploratory testing, but at the same time retains some of the advantages of exploratory testing like mimicking the user experience and getting creative with testing. In session based testing, testing is carried out in time-boxed uninterrupted sessions, testing against a charter, and requires testers to report on testing that took place during the session. The charter indicates the mission, the areas of the software to test, the test designs, bugs found, etc. So session based testing emphasizes clearly documenting activities and taking notes in a session.
So, that was all about agile testing and testing approaches. To conclude, to align with testing in an agile environment, the key things to keep in mind are
- Get involved in the development process as early as possible.
- Test frequently and continuously.
Hope the article helped you understand agile testing more. and help you go the agile way!
How much is a great User Experience worth to you?
Browsee helps you understand your user's behaviour on your site. It's the next best thing to talking to them.


